RESECT Data collection is now closed.
Congratulations to all collaborators: 200 sites completed & >19000 cases assessed.
Background:
Superficial bladder cancer, known as non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) is the most common type of bladder cancer. It is expensive to manage. This is because there is a high burden of recurrent disease after initial treatment and need for long term surveillance for recurrence.
The most important step in the diagnosis and treatment of NMIBC is the first surgical procedure called the transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT). This procedure is crucial in properly grading and staging the disease (thus determining the next appropriate treatment) and in potentially providing a curative treatment for certain cases. There is evidence that the quality of the TURBT operation, and the use of a single instillation postoperative intravesical chemotherapy (SI-IVC) with Mitomycin-C, can reduce cancer recurrence rates and progression to more invasive cancer. Despite this, there is anecdotal evidence that the quality of TURBT surgery and the usage of intravesical chemotherapy varies widely between hospitals and thus may result in worse outcomes for some.
Aims:
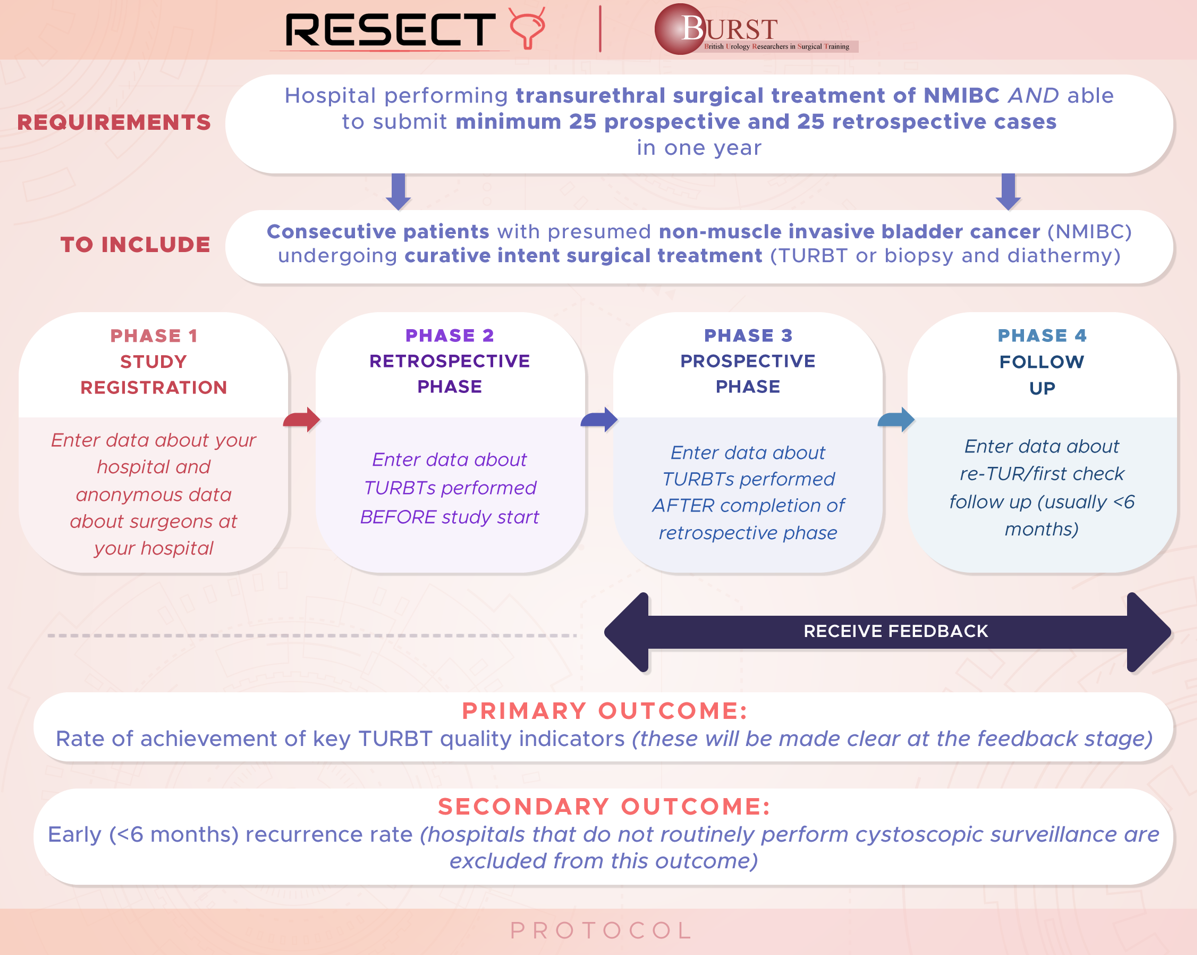
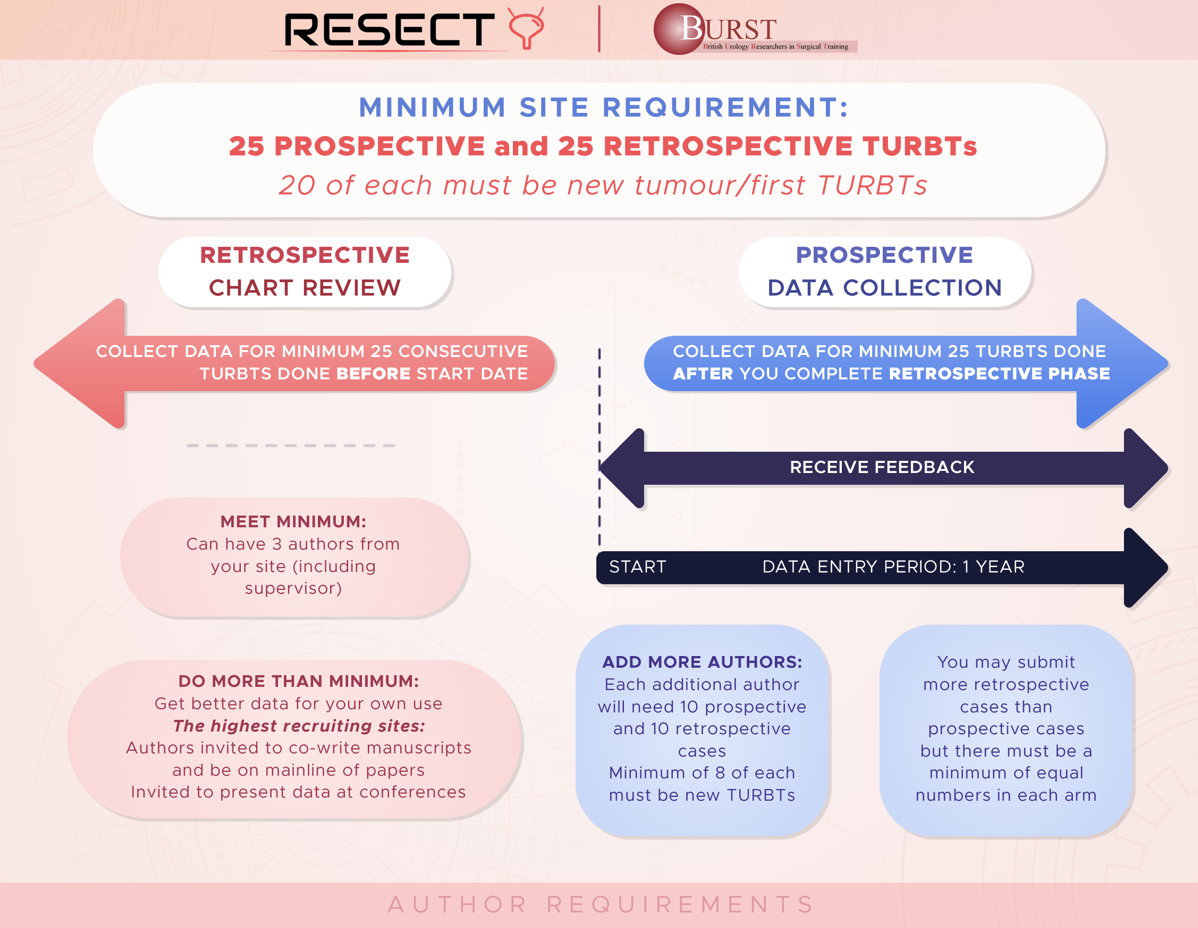
To conduct a retrospective and prospective, multicentre, international study of urological practice of the management of NMIBC. The primary objective is to determine if audit and feedback can improve the quality of TURBT surgery and reduce early recurrence rates. We will measure the achievement of TURBT quality indicators across hospitals, regions and countries and compare these against evidence-based recommendations. We aim to determine if any hospital, service, training, or technical factors impact the achievement of quality indicators and/or early recurrence rates. We aim to use these data to present hospital and clinician performance back to surgeons, as a method of driving quality improvement. The timing of feedback to different hospitals will be varied randomly so that we can determine if the feedback is having an impact on audit performance.
RESECT aims:
- Does reporting and comparing our TURBT quality make us do it better?
- What things should we measure to determine TURBT quality?
- What rate of achievement should we aim for in our practice?
- What factors are associated with better achievement of TURBT quality?